Does The Camera In My Samsung J3 Have Image Stabilization
4K resolution refers to a horizontal display resolution of approximately four,000 pixels.[1] Digital telly and digital cinematography usually utilize several different 4K resolutions. In television and consumer media, 3840 ×2160 (4K UHD) is the dominant 4K standard, whereas the movie projection industry uses 4096 ×2160 (DCI 4K).
The 4K telly market place share increased equally prices barbarous dramatically during 2014[two] and 2015.

Comparison of mutual circulate resolutions

4K standards and terminology [edit]
The term "4K" is generic and refers to any resolution with a horizontal pixel count of approximately 4,000.[3] :2 Several unlike 4K resolutions have been standardized by diverse organizations.
The terms "4K" and "Ultra Hd" are used more than widely in marketing than "2160p". While typically referring to motility pictures, some digital camera vendors accept used the term "4K photo" for still photographs, making it appear like an especially loftier resolution even though 3840×2160 pixels equal approximately 8.three megapixels, which is not particularly high for still photographs.[four]
DCI Digital Cinema Organization Specification [edit]

Comparing of DCI and UHD resolutions
In 2005, Digital Movie theater Initiatives (DCI), a prominent standards organization in the cinema industry, published the Digital Cinema System Specification. This specification establishes standardized 2K and 4K container formats for digital picture palace production, with resolutions of 2048 × 1080 and 4096 × 2160 respectively.[v] : §4.3.ane The resolution of the video content inside follows the SMPTE 428-ane standard,[five] : §iii.two.ane which establishes the following resolutions for a 4K distribution:[6] : 6
- 4096 ×2160 (full frame, 256∶135 or ≈1.ninety∶one aspect ratio)
- 3996 ×2160 (flat crop, i.85∶ane aspect ratio)
- 4096 ×1716 (CinemaScope ingather, ≈2.39∶1 aspect ratio)
2K distributions can have a frame rate of either 24 or 48FPS, while 4K distributions must have a frame rate of 24FPS.[5] : §3.1.4.two Some articles claim that the terms "2K" and "4K" were coined by DCI and refer exclusively to the 2K and 4K formats defined in the DCI standard.[7] Yet, usage of these terms in the picture palace manufacture predates the publication of the DCI standard,[8] [9] [x] [11] and they are by and large understood every bit casual terms for whatever resolution approximately 2000 or 4000 pixels in width, rather than names for specific resolutions.[three] :two [12] : 109
SMPTE UHDTV standard [edit]
In 2007, the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers published SMPTE ST 2036-1, which defines parameters for 2 UHDTV systems called UHDTV1 and UHDTV2.[13] [14] The standard defines the following characteristics for these systems:
- A resolution of 3840 × 2160 (UHDTV1) or 7680 × 4320 (UHDTV2)[14] : §5.2
- Square (1∶1) pixels, for an overall image attribute ratio of 16∶nine[xiv] : §5.1
- A framerate of 23.976, 24, 25, 29.97, xxx, 50, 59.94, 60, 100, 119.88, or 120Hz with progressive scan[xiv] : §ane.two
- RGB, Y′CBCR iv:four:four, 4:2:2, or 4:two:0 pixel encoding[14] : §7.7
- xbpc (30bit/px) or 12bpc (36fleck/px) colour depth[fourteen] : §ane.ii
- Colorimetry characteristics as divers in the standard, including color primaries, quantization parameters, and the electro-optical transfer role. These are the same characteristics after standardized in ITU-R BT.2020. UHDTV1 systems are permitted to employ BT.709 color primaries up to 60Hz.[14] : §6.2
ITU-R UHDTV standard [edit]
In 2012, the International Telecommunication Union, Radiocommunication Sector published Recommendation ITU-R BT.2020, too known as the Ultra High Definition Tv set (UHDTV) standard.[15] It adopts the aforementioned image parameters defined in SMPTE ST 2036–1.[16]
Although the UHDTV standard does not ascertain any official names for the formats information technology defines, ITU typically uses the terms "4K", "4K UHD", or "4K UHDTV" to refer to the 3840 × 2160 system in public announcements and press releases ("8K" for the 7680 × 4320 system).[17] In some of ITU'south other standards documents, the terms "UHDTV1" and "UHDTV2" are used every bit shorthand.[xviii]
CEA Ultra HD [edit]
In Oct 2012, the Consumer Electronics Association (CEA) announced their definition of the term Ultra High-Definition (or Ultra Hard disk) for utilize with marketing consumer brandish devices.[19] CEA defines an Ultra Hard disk production equally a Idiot box, monitor, or projector with the post-obit characteristics:[twenty]
- A resolution of 3840 × 2160 or larger
- An aspect ratio of 1.77∶1 (16∶9) or wider
- Back up for color depth of 8bpc (24bit/px) or college
- At least one HDMI input capable of supporting 3840 × 2160 at 24, 30, and 60Hz progressive scan (though not necessarily with RGB / Y′CBCR 4:iv:4 color), and HDCPii.ii
- Capable of processing images according to the color space defined in ITU-R BT.709
- Capable of upscaling HD content (i.eastward. 720p / 1080p)
The CEA definition does let manufacturers to use other terms—such as 4K—alongside the Ultra HD logo.[3] :9 Since the resolution in CEA's definition is only a minimum requirement, displays with higher resolutions such as 4096 × 2160 or 5120 × 2880 also qualify equally "Ultra HD" displays, provided they meet the other requirements.
2160p resolution [edit]
Some 4K resolutions, like 3840 × 2160 , are oftentimes casually referred to equally 2160p.[21] [22] [23] This proper name follows from the previous naming convention used past HDTV and SDTV formats, which refer to a format by the number of pixels/lines along the vertical axis (such equally "1080p" for 1920 × 1080 progressive scan, or "480i" for the 480-line interlaced SDTV formats) rather than the horizontal pixel count (≈4000 or "4K" for 3840 × 2160 ).
The term "2160p" could be applied to whatsoever format with a tiptop of 2160 pixels, but it is most normally used in reference to the 4K UHDTV resolution of 3840 × 2160 due to its association with the well-known 720p and 1080p HDTV formats. Although 3840 × 2160 is both a 4K resolution and a 2160p resolution, these terms cannot always be used interchangeably since non all 4K resolutions are 2160 pixels tall, and not all 2160p resolutions are ≈4000 pixels wide. However, some companies have begun using the term "4K" to describe devices with support for a 2160p resolution, even if it is not close to 4000 pixels wide. For case, many "4K" dash cams only support a resolution of 2880 × 2160 (four∶3);[24] [25] although this is a 2160p resolution, it is not a 4K resolution. Conversely, Samsung released a 5120 × 2160 (64∶27) Television receiver, just marketed it as a "4K" Telly despite its 5K-class resolution.[26] [27]
M+ or RGBW TV controversy [edit]
In 2015, LG Display appear the implementation of a new technology called M+ which is the add-on of white subpixel along with the regular RGB dots in their IPS panel engineering science.[28] The media and cyberspace users later called this "RGBW" TVs because of the white sub pixel.
Virtually of the new Chiliad+ technology was employed on 4K TV sets which led to a controversy after tests showed that the improver of a white sub pixel replacing the traditional RGB structure would reduce the resolution by around 25%. Later tests done by Intertek in which the technical aspects of LG M+ TVs were analyzed and they ended that "the addressable resolution display is 2,880 X 2,160 for each red, green, blue", in other words, the LG TVs were technically ii.8K every bit it became known in the controversy.[29] [30] Although LG Display has adult this technology for use in notebook display, outdoor and smartphones, it is more than popular in the TV market place due to the supposed 4K UHD marketed resolution but nevertheless being incapable of achieving true 4K UHD resolution as divers by the CTA as 3840x2160 active pixels with 8-bit per color. This negatively impacts the rendering of text, making it a scrap fuzzier, which is especially noticeable when a TV is used as a PC monitor.[31] [32] [33] [34] [35]
CinemaWide 4K [edit]
In 2019, Sony was granted the CinemaWide trademark past the European union Intellectual Property Office (EUIPO), in which the trademark covers 'Class 9' electronic devices, including smartphones.[36] According to Sony and SID,[37] the standard defines a CinemaWide 4K product with the post-obit characteristics:
- A resolution of 3840 × 1644 or larger
- An aspect ratio of 21∶9
- Capable of playing back 4K resolution video (2160p) in an aspect ratio of 21∶ix
- Capable of upscaling non-4K content (i.east. 720p / 1080p)[38]
Sony Xperia smartphones are the most widely known products that equipped with CinemaWide 4K brandish, such as Xperia 1, Xperia 1 Two and Xperia 1 III.
Adoption [edit]
Video sharing website YouTube and the telly manufacture take adopted 3840 ×2160 as their 4K standard.[39] [40] Equally of 2014[update], 4K content from major broadcasters remained express.[41] On April 11, 2013, Bulb Television receiver created by Canadian serial entrepreneur Evan Kosiner became the get-go broadcaster to provide a 4K linear channel and VOD content to cable and satellite companies in North America.[42] [43] [44] [45] The channel is licensed past the Canadian Radio-Television and Telecommunication Commission to provide educational content.[46] However, 4K content is becoming more widely available online[ when? ] including on Apple Television set, YouTube, Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon.[47] [48] By 2013, some UHDTV models were available to general consumers in the range of US$600.[49] [fifty] Equally of 2015[update], prices on smaller computer and television panels had dropped below US$400.[51]
ATSC [edit]
On March 26, 2013, the Advanced Television Systems Committee appear new proposals of a new standard chosen ATSC iii.0 which would implement UHD broadcasts at resolutions of up to 3840 × 2160 or 7680 × 4320 .[52] [53] [54] [55] The standard would also include framerates of up to 120Hz, HEVC encoding, wide color gamut, as well as high dynamic range.[56] [57] [58]
DVB [edit]
In 2014, the Digital Video Dissemination Project released a new fix of standards intended to guide the implementation of loftier resolution content in broadcast television. Dubbed DVB-UHDTV, it establishes two standards, known every bit UHD-1 (for 4K content) and UHD-2 (for 8K content). These standards apply resolutions of 3840 ×2160 and 7680 ×4320 respectively, with framerates of up to 60Hz, color depth upward to tenbpc (xxxscrap/px), and HEVC encoding for transmission.[59] DVB is currently focusing on the implementation of the UHD-1 standard.[60]
DVB finalized UHD-1 Stage ii in 2016, with the introduction of service past broadcasters expected in 2017. UHD-1 Phase 2 adds features such equally loftier dynamic range (using HLG and PQ at 10 or 12 bits), broad color gamut (BT. 2020/2100 colorimetry), and high frame rate (up to 120Hz).[61] [60]
Video streaming [edit]
YouTube, since 2010,[62] and Vimeo let a maximum upload resolution of 4096 × 3072 pixels (12.6 megapixels, attribute ratio 4:iii).[63] [64] Vimeo'south 4K content is currently limited to more often than not nature documentaries and tech coverage.[65] [66]
High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC or H.265) should allow streaming 4K content with a bandwidth of 20 to 30 Mbit/southward.[67]
In Jan 2014, Naughty America launched the first developed video service streaming in 4K.[68] [69]
Mobile phone cameras [edit]
The get-go mobile phones to be able to tape at 2160p ( 3840 × 2160 ) were released in tardily 2013, including the Samsung Galaxy Note 3, which is able to tape 2160p at 30 frames per 2nd.
In the year 2014, the OnePlus Ane was released with the choice to record DCI 4K ( 4096 × 2160 ) at 24 frames per 2nd, as well as LG G3 and Samsung Galaxy Note 4 with optical image stabilization.
In the year 2015, Apple announced the iPhone 6s was released with the 12Mpx camera that has the option to record 4K at 25 or xxx frames per second.
In the years 2017 and 2018, mobile phone chipsets reached sufficient processing power that mobile phone vendors started releasing mobile phones that let recording 2160p footage at 60 frames per second for a smoother and more realistic advent.[70]
History [edit]

Samsung UN105S9 105-inch (ii,700 mm) ultra-loftier-definition 4K television
In 1984, Hitachi released the CMOS graphics processor ARTC HD63484, which was capable of displaying up to 4K resolution when in monochrome fashion.[71] The resolution was targeted at the bit-mapped desktop publishing market.[71] The first commercially available 4K photographic camera for cinematographic purposes was the Dalsa Origin, released in 2003.[72] [73] 4K technology was developed by several enquiry groups in universities around the world, such as University of California, San Diego, CALIT2, Keio University, Naval Postgraduate School and others that realized[74] several demonstrations in venues such as IGrid in 2004 and CineGrid. YouTube began supporting 4K for video uploads in 2010 as a result of leading manufacturers producing 4K cameras.[75] Users could view 4K video by selecting "Original" from the quality settings until Dec 2013, when the 2160p option appeared in the quality carte.[76] In November 2013, YouTube began to use the VP9 video compression standard, proverb that information technology was more suitable for 4K than Loftier Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC). Google, which owns YouTube, developed VP9.[75]
Theaters began projecting movies at 4K resolution in 2011.[77] Sony was offering 4K projectors as early as 2004.[78] The beginning 4K home theater projector was released past Sony in 2012.[79] Despite this, few finished films accept 4K resolution as of 2019. Even for movies and TV shows shot using 6K or 8K cameras, almost all finished films are edited in HD resolution and enlarged to fit a 4K format.[fourscore]
Sony is ane of the leading studios promoting UHDTV content, as of 2013[update] offer a little over 70 flick and television titles via digital download to a specialized player that stores and decodes the video. The large files (≈fortyGB), distributed through consumer broadband connections, heighten concerns about data caps.[81]
In 2014, Netflix began streaming House of Cards, Breaking Bad,[82] and "some nature documentaries" at 4K to compatible televisions with an HEVC decoder. Most 4K televisions sold in 2013 did non natively support HEVC, with nearly major manufacturers announcing back up in 2014.[83] Amazon Studios began shooting their total-length original series and new pilots with 4K resolution in 2014.[84] They are now currently available though Amazon Video.[85]
In March 2016 the first players and discs for Ultra Hard disk drive Blu-ray—a physical optical disc format supporting 4K resolution and high-dynamic-range video (HDR) at 60 frames per 2nd—were released.[86]
On August ii, 2016, Microsoft released the Xbox One S, which supports 4K streaming and has an Ultra HD Blu-ray disc drive, but does non back up 4K gaming.[87] On November 10, 2016, Sony released the PlayStation 4 Pro, which supports 4K streaming and gaming,[88] though many games use checkerboard rendering or are upscaled 4K.[89] On Nov 7, 2017, Microsoft released the Xbox Ane X, which supports of 4K streaming and gaming,[90] though not all games are rendered at native 4K.[91]
Home video project [edit]
Though experiencing rapid price drops beginning in 2013 for viewing devices, the home cinema digital video projector market saw little expansion, with only a few manufacturers (only Sony every bit of 2015[update]) offering express 4K-capable lineups, with native 4K projectors commanding five-figure price tags well into 2015 before finally breaking the Us$10,000 bulwark.[92] Critics country that at normal direct-view panel size and viewing distances, the extra pixels of 4K are redundant at the ability of normal human being vision.[ commendation needed ] Projection home cinemas, on the other manus, employ much larger screen sizes without necessarily increasing viewing distance to scale. JVC has used a technique known as "e-shift" to extrapolate extra pixels from 1080p sources to display 4K on screens through upscaling or from native 4K sources at a much lower price than native 4K projectors.[93] This engineering of not-native 4K entered its 4th generation for 2016.[94] [95] [96] JVC used this same technology to provide 8K flying simulation for Boeing that met the limits of xx/25 visual acuity.[97]
Pixel shifting, as described here, was pioneered in the consumer infinite by JVC, and later in the commercial space by Epson. That said, it is non the aforementioned thing as "true" 4K. More recently, some DLP projectors claim 4K UHD (which the JVCs and Epsons do not merits).
Every bit noted to a higher place, DCI 4K is 4096 ×2160, while 4K UHD is 3840 ×2160, producing a slight difference in aspect ratio rather than a meaning difference in resolution. Traditional displays, such as LCD or OLED, are 3840 pixels across the screen, with each pixel being 1/3840th of the screen width. They practise not overlap—if they did, they would endure reduced item. The diameter of each pixel is basically i/3840th of the screen width or i/2160th of the screen meridian - either gives the same size pixel. That 3840 ×2160 works out to viii.3 megapixels, the official resolution of 4K UHD (and therefore Blu-ray UHD discs).
The 4K UHD standard does non specify how large the pixels are, then a 4K UHD projector (Optoma, BenQ, Dell, et al.) counts because these projectors have a 2718 × 1528 pixel structure. Those projectors process the true 4K of data and project it with overlapping pixels, which is what pixel shifting is. Unfortunately, each of those pixels is far larger: each 1 has 50% more expanse than true 4K. Pixel shifting projectors project a pixel, shift it up to the right, by a one-half diameter, and projection it over again, with modified data, but that second pixel overlaps the first.
In other words, pixel shifting cannot produce side by side vertical lines of RGBRGB or other colors where each line is ane pixel (i/3840th of the screen) wide. Adjacent red and green pixels would end up looking like yellow, with a fringe on one side of red, on the other of dark-green - except that the next line of pixels overlaps equally well, changing the colour of that fringe. 4K UHD or 1080p pixel shifting cannot reveal the fine detail of a true 4K projector such as those Sony ships (business, education and home markets). Besides, JVC has one true 4K projector priced at $35,000 (every bit of mid-2017).
So while 4K UHD appears like it has a pixel structures with 1/iv the area of 1080p, that does not happen with pixel shifting. Only a true 4K projector offers that level of resolution. This is why "true" 4K projectors toll so much more than 4K UHD projectors with otherwise similar feature sets. They produce smaller pixels, finer resolution, no compromising of detail or color from overlapping pixels. By comparison, the slight departure in aspect ratio between DCI and 3840 × 2160 pixel displays without overlap is insignificant relative to the corporeality of item.
Some companies like Kaleidescape offering media servers that allow for 4K UHD Blu-ray movies with high dynamic range in a home theater.[98]
Dissemination [edit]
In November 2014, United states satellite provider DirecTV became the first pay Tv set provider to offer access to 4K content, although express to selected video-on-need films.[99] In Baronial 2015, British sports network BT Sport launched a 4K feed, with its first broadcast existence the 2015 FA Community Shield football match. Two production units were used, producing the traditional broadcast in high-definition, and a divide 4K broadcast. As the network did not desire to mix 4K footage with upconverted HD footage, this telecast did not characteristic traditional studio segments at pre-game or half-time, but those hosted from the stadium by the match commentators using a 4K camera. BT envisioned that if viewers wanted to watch studio analysis, they would switch to the Hd broadcast and and then back for the game. Footage was compressed using H.264 encoders and transmitted to BT Tower, where it was then transmitted back to BT Sport studios and decompressed for distribution, via 4K-uniform BT TV set up-peak boxes on an eligible BT Infinity internet program with at least a 25 Mbit/s connection.[100] [101]
In late 2015 and Jan 2016, three Canadian goggle box providers – including Quebec-based Vidéotron, Ontario-based Rogers Cable, and Bell Fibe TV, announced that they would begin to offer 4K compatible set-superlative boxes that can stream 4K content to subscribers over gigabit internet service.[102] [103] On October v, 2015, alongside the announcement of its 4K set-peak box and gigabit internet, Canadian media conglomerate Rogers Communications announced that information technology planned to produce 101 sports telecasts in 4K in 2016 via its Sportsnet partition, including all Toronto Blue Jays home games, and "marquee" National Hockey League games commencement in January 2016. Bell Media announced via its TSN partition a slate of 4K telecasts to brainstorm on January 20, 2016, including selected Toronto Raptors games and regional NHL games.[104] [105] [106]
On January xiv, 2016, in cooperation with BT Sport, Sportsnet broadcast the first ever NBA game produced in 4K – a Toronto Raptors/Orlando Magic game at O2 Arena in London, England. On January 20, also during a Raptors game, TSN presented the start live 4K telecast produced in North America.[102] [104] [107] Three days later on, Sportsnet presented the offset NHL game in 4K.[108]
Dome Productions, a joint venture of Bell Media and Rogers Media (the respective owners of TSN and Sportsnet), synthetic a "side-by-side" 4K mobile production unit shared past Sportsnet and TSN's first 4K telecasts; it was designed to operate alongside a separate HD truck and utilize cameras capable of output in both formats.[109] For the opening game of the 2016 Toronto Bluish Jays flavor, Dome synthetic "Trillium" – a production truck integrating both 4K and 1080i loftier-definition units.[110] Bong Media's CTV also broadcast the 2016 Juno Awards in 4K as the first awards show presented in the format.[111]
In Feb 2016, Univision trialed 4K by producing a closed circuit telecast of a football game friendly between the national teams of Mexico and Senegal from Miami in the format. The broadcast was streamed privately to several special viewing locations. Univision aimed to develop a 4K streaming app to publicly televise the final of Copa América Centenario in 4K.[112] [113] [114] In March 2016, DirecTV and CBS Sports announced that they would produce the "Amen Corner" supplemental coverage from the Masters golf game tournament in 4K.[115] [116]
In late 2016, Telus Tv set announced that they would begin to offer 4K compatible set-height boxes.[117]
Afterward having trialed the technology in limited matches at the 2013 FIFA Confederations Cup,[118] and the 2014 FIFA Globe Cup (via private tests and public viewings in the host urban center of Rio de Janeiro),[119] the 2018 FIFA World Loving cup was the beginning FIFA World Cup in which all matches were produced in 4K. Host Broadcasting Services stated that at least 75% of the broadcast cutting on each lucifer would come from 4K cameras (covering the majority of main angles), with instant replays and some camera angles being upconverted from 1080p sources. These broadcasts were made bachelor from selected rightsholders, such equally the BBC in the United kingdom, and selected idiot box providers in the United States.[120] [121] [122]
Resolutions [edit]
| Examples of some 4K resolutions used in displays and media | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Format | Resolution | Aspect Ratio | Pixels |
| - | 4096 ×3072 | 1.33∶1 (four∶3) | 12,582,912 |
| - | 4096 ×2560 | 1.60∶one (16∶10) | 10,485,760 |
| - | 4096 ×2304 | i.77∶i (16∶9) | nine,437,184 |
| DCI 4K (full frame) | 4096 ×2160 | ≈one.ninety∶1 (256∶135) | 8,847,360 |
| DCI 4K (CinemaScope cropped) | 4096 ×1716 | ≈2.39∶1 (1024∶429) | 7,020,544 |
| DCI 4K (flat cropped) | 3996 ×2160 | one.85∶i (≈37∶xx) | 8,631,360 |
| WQUXGA | 3840 ×2400 | 1.threescore∶ane (16∶10) | 9,216,000 |
| 4K UHD | 3840 ×2160 | 1.77∶ane (16∶nine) | 8,294,400 |
| - | 3840 ×1600 | 2.40∶1 (12∶5) | 6,144,000 |
| - | 3840 ×1080 | 3.55∶1 (32∶nine) | four,147,200 |
3840 ×2160 [edit]
The resolution of 3840 × 2160 is the dominant 4K resolution in the consumer media and display industries. This is the resolution of the UHDTV1 format defined in SMPTE ST 2036–1,[14] as well equally the 4K UHDTV format defined by ITU-R in Rec. 2020,[15] and is also the minimum resolution for CEA's definition of Ultra Hard disk displays and projectors.[20] The resolution of 3840 × 2160 was likewise chosen past the DVB project for their 4K broadcasting standard, UHD-one.[60]
This resolution has an aspect ratio of 16∶9, with viii,294,400 full pixels. Information technology is exactly double the horizontal and vertical resolution of 1080p ( 1920 × 1080 ) for a total of 4 times as many pixels, and triple the horizontal and vertical resolution of 720p ( 1280 × 720 ) for a total of 9 times as many pixels. It is sometimes referred to as "2160p", based on the naming patterns established by the previous 720p and 1080p HDTV standards.
In 2013, televisions capable of displaying UHD resolutions were seen by consumer electronics companies as the next trigger for an upgrade bike afterward a lack of consumer interest in 3D television.[123]
4096 ×2160 [edit]
This resolution is used mainly in digital cinema product, and has a full of 8,847,360 pixels with an aspect ratio of 256∶135 (≈xix∶ten). It was standardized equally the resolution of the 4K container format defined by Digital Cinema Initiatives in the Digital Cinema System specification, and is the native resolution of all DCI-compliant 4K digital projectors and monitors.[five] The DCI specification allows several unlike resolutions for the content inside the container, depending on the desired aspect ratio. The allowed resolutions are defined in SMPTE 428-1:[5] : §3.2.1 [half-dozen] : p. 6
- 4096 ×2160 (total frame, 256∶135 or ≈1.xc∶1 attribute ratio)
- 3996 ×2160 (flat crop, 1.85∶1 aspect ratio)
- 4096 ×1716 (CinemaScope crop, ≈2.39∶1 aspect ratio)
The DCI 4K standard has twice the horizontal and vertical resolution of DCI 2K ( 2048 × 1080 ), with iv times equally many pixels overall.
Digital movies made in 4K may exist produced, scanned, or stored in a number of other resolutions depending on what storage aspect ratio is used.[124] [125] In the digital movie house production concatenation, a resolution of 4096 × 3112 is oft used for acquiring "open gate" or anamorphic input fabric, a resolution based on the historical resolution of scanned Super 35 mm pic.[126]
Other 4K resolutions [edit]
Various other non-standardized 4K resolutions have been used in displays, including:
- 4096 ×2560 (i.60∶1 or 16∶10); this resolution was used in the Canon DP-V3010, a 30-inch (76 cm) 4K reference monitor designed for reviewing cinema footage in postal service-production, released in 2013.[127]
- 4096 ×2304 (1.77∶1 or 16∶ix); this resolution was used in the 21.v-inch (55 cm) LG UltraFine 22MD4KA 4K monitor, jointly announced past LG and Apple in 2016[128] and used in the 21.5" 4K Retina iMac computer.
- 3840 ×2400 (1.sixty∶1 or xvi∶10); this resolution was used in the 22.2-inch (56 cm) IBM T220 and T221 monitors, released in 2001 and 2002 respectively. This resolution is also referred to as "WQUXGA", and is iv times the resolution of WUXGA (1920 ×1200).[129]
- 3840 ×1600 (2.40∶one or 12∶5); a number of computer monitors with this resolution take been produced, the first being the 37.v-inch (95 cm) LG 38UC99-Westward released in 2016. This resolution is equivalent to WQXGA (2560 ×1600) extended in width by 50%, or 3840 ×2160 reduced in height by ≈26%.[130] LG refers to this resolution as "WQHD+" (Wide Quad HD+),[131] while Acer uses the term "UW-QHD+" (Ultra-wide Quad Hard disk+)[132] and some media outlets have used the term "UW4K" (Ultra-wide 4K).[133] [134]
- 3840 ×1080 (iii.55∶one or 32∶9); this resolution was first used in the Samsung C49HG70, a 49-inch (120 cm) curved gaming monitor released in 2017. This resolution is equivalent to dual 1080p displays (1920 ×1080) side-by-side, but with no border interrupting the image. Information technology is also exactly one one-half of a 4K UHD (3840 ×2160) display. Samsung refers to this resolution as "DFHD" (Dual Total HD).[135]
Recording [edit]

Item benefit [edit]
The master advantage of recording video at the 4K standard is that fine spatial particular is resolved well.[136] Private withal frames extracted from 3840×2160-pixel video footage can human activity as eight.3 megapixel all the same photographs, while only 2.1 megapixels at 1080p and 0.9 megapixels at 720p. If the final video quality is reduced to 2K from a 4K recording, more than detail is apparent than would have been accomplished from a native 2K recording.[136] Increased fineness and contrast is so possible with output to DVD and Blu-ray.[137] Some cinematographers tape at 4K with the Super 35 moving picture format to offset whatsoever resolution loss that may occur during video processing.[138]
Chroma subsampling [edit]
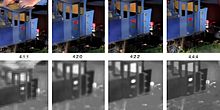
In full size, this epitome shows the difference betwixt four subsampling schemes. Note how like the color images appear. The lower row shows the resolution of the color information.
Many consumer electronics such as mobile phones store video footage in Y′CBCR format with four:ii:0 blush subsampling, which records colour information at merely 1 quarter the resolution equally the brightness information.[139] For 3840 × 2160 video, this means that the colour information is only stored at 1920 × 1080 .[140] [141]
Chip rates [edit]
Consumer cameras and mobile phones tape 2160p footage at much college bit rates (unremarkably 50 to 100Mbit/s) than 1080p (ordinarily ten to 30Mbit/s). This higher bit rate reduces the visibility of compression artifacts, even if viewed on monitors with a lower resolution than 2160p.
Come across also [edit]
- 1080p Full Hard disk – digital video format with a resolution of 1920 × 1080
- List of 4K video recording devices
- 2K resolution – digital video formats with a horizontal resolution of around 2,000 pixels
- 5K resolution – digital video formats with a horizontal resolution of around 5,000 pixels, aimed at non-boob tube computer monitor usage
- 8K resolution – digital video formats with a horizontal resolution of effectually viii,000 pixels
- 10K resolution – digital video formats with a horizontal resolution of around 10,000 pixels
- 16K resolution – experimental VR format
- Aspect ratio (image) – proportional relationship between an prototype's width and height
- Digital movie theatre
- Graphics display resolution
- High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) – video standard that supports 4K & 8K UHDTV and resolutions upward to 8192 × 4320
- Rec. 2020 – ITU-R recommendation for UHDTV, defining formats with resolutions of 4K ( 3840 × 2160 ) and 8K ( 7680 × 4320 )
- Ultra-high-definition television (UHDTV) – various standards for high-resolution goggle box
- Ultrawide formats
References [edit]
- ^ Goulekas, Karen (2001). Visual Effects in a Digital World . Morgan Kaufmann. p. 587. ISBN9780080520711.
4K resolution: A general term referring to any digital image containing an X resolution of approximately 4096 pixels.
- ^ "Beginning Quarter 2015 4K TV Growth Potent Every bit Overall LCD TV Shipments Slow, IHS Says". IHS Inc. 8 June 2015. Archived from the original on 12 June 2015. Retrieved Nov 24, 2015.
- ^ a b c CEA Marketplace Research Report—Ultra Loftier-Definition: Land of the Industry, Consumer Electronics Association, Baronial 2013
- ^ "What is 4K Photo? Panasonic'southward camera tech explained - Pocket-li". www.pocket-lint.com. 3 Jan 2017. Retrieved 24 October 2021.
- ^ a b c d e "Digital Cinema Organisation Specification Version 1.ii with Errata as of thirty August 2012 Incorporated" (PDF). Digital Movie house Initiatives, LLC. October x, 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-05-27. Retrieved April 29, 2018.
- ^ a b SMPTE 428-1-2006: D-Cinema Distribution Master - Epitome Characteristics, Order of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE), September 29, 2006
- ^ "4K vs. UHD: What'southward the difference? – ExtremeTech". Archived from the original on 22 December 2018.
- ^ Swinson, Peter (November 2005). "DCI and Other Film Formats" (PDF). Peter Swinson Associates, Limited. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 December 2018. Retrieved Apr 29, 2018.
- ^ "Defining 2K & 4K". Cinematography Mailing List. March 25, 2004. Archived from the original on 22 Dec 2018. Retrieved Apr 29, 2018.
- ^ "2K Film Resolution". CGSociety. June 6, 2003. Archived from the original on 22 December 2018.
- ^ "what resolution/ratio/frame rate?". CreativeCOW.net. September 25, 2002. Retrieved April 29, 2018.
- ^ "WEAPON/EPIC-W 8K S35 Functioning Guide v7.0" (PDF). Red Digital Cinema Camera Company. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 28, 2018. Retrieved May 28, 2018.
- ^ "OV 2036-0:2015: Ultra High Definition Television — Overview for the SMPTE ST 2036 Document Suite". Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE). March 27, 2015. doi:10.5594/SMPTE.OV2036-0.2015.
- ^ a b c d e f g h SMPTE ST 2036-1:2014, Society of Motion Picture and Idiot box Engineers (SMPTE), October 13, 2014
- ^ a b "Ultra High Definition Television: Threshold of a new age". ITU-R. May 24, 2012. Retrieved April 29, 2018.
- ^ "ITU-R Recommendation BT.2020-2: Parameter values for ultra-loftier definition television systems for production and international plan exchange" (PDF). ITU-R. Oct 2015. Retrieved April 29, 2018.
- ^ "New ITU reports aid shape adjacent Idiot box revolution: High Dynamic Range (HDR)". ITU News. ITU-R. November 21, 2017. Retrieved April 29, 2018.
- ^ "ITU-R Recommendation BT.2077-two: Real-time serial digital interfaces for UHDTV signals" (PDF). ITU-R. June 2017. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2018-04-thirty. Retrieved April 29, 2018.
- ^ "Consumer Electronics Industry Announces Ultra Loftier-Definition". Digital Photography Review. October 19, 2012. Retrieved April 29, 2018.
- ^ a b "CEA Updates Characteristics for Ultra Loftier-Definition Displays". Consumer Electronics Association (CEA). June 24, 2014. Retrieved April 29, 2018.
- ^ Nick Pino, Jon Porter (March 8, 2018). "4K and Ultra HD: Everything y'all need to know most the hot new resolution". Tech Radar. Archived from the original on August 19, 2018. Retrieved September 1, 2018.
- ^ Thomas, Alexander. "Merely how useful is 2160p aka 4K?". Archived from the original on November 26, 2017. Retrieved September 1, 2018.
- ^ Morrison, Geoffrey. "Resolution confusion: What do 2K, 4K, 1080p, UHD all mean?". CNET . Retrieved 2020-07-13 .
- ^ "STERIO 4K 2880x2160/P24 Dash Cam". Amazon.com. Archived from the original on September 1, 2018.
Super HD 4K 2880x2160P Resolution and 170 Degree A+ Ultra Broad Bending---Record every detail with the latest technique of auto video shooting.
- ^ "AUKEY 4K Nuance Cam". Amazon.com. Archived from the original on September 1, 2018. Retrieved September 1, 2018.
An advanced prototype sensor and super-wide field of view capture everything in ultra-sharp 4K(2880 ten 2160 @24fps) video with HDR.
- ^ "105" CLASS 105S9 CURVED 4K UHD SMART Idiot box". samsung.com. Archived from the original on 2017-09-09. Retrieved 2018-09-01 .
Type: Curved 4K UHD TV; Resolution: 5120 x 2160
- ^ Wheatley, Mike (July 30, 2014). "Samsung & LG Begin Sales of 105" 21:nine 4K, Nay, 5K Television receiver". HDTVtest. Archived from the original on 2017-09-09. Retrieved September ane, 2018.
- ^ "A whole new world of color with LG'due south RGBW technology". m.engineeringnews.co.za . Retrieved 2020-07-12 .
- ^ "What is RGBW Goggle box?". news.samsung.com . Retrieved 2020-07-13 .
- ^ "Some LG 4K LCD TVs still deliver only two.8K resolution". TechHive. 2017-12-26. Retrieved 2020-07-xiii .
- ^ "What is the Resolution?". RTINGS.com . Retrieved 2020-07-12 .
- ^ "How LG uses fuzzy math to characterization some of its LCD TVs every bit 4K". TechHive. 2016-09-21. Retrieved 2020-07-12 .
- ^ "LG 4K LCD TVs Continue Controversial RGBW Tech". HD Guru. 2017-01-27. Retrieved 2020-07-12 .
- ^ "The departure betwixt 4K and UHD, and the inflow of UHD Premium certification : Buying a 4K Boob tube: What you demand to know about HDCP two.2, HDMI 2.0, HEVC & UHD". www.hardwarezone.com.sg . Retrieved 2020-07-12 .
- ^ "Fake-K: RGBW LED TV Spoils 4K UHD Resolution & Color". HDTV Test . Retrieved 2020-07-13 .
- ^ "Sony Xperia XZ4 to Sport 'CinemaWide' Display, Trademark Filing Tips". gadgets.ndtv.com . Retrieved 2021-07-28 .
- ^ "Xperia i Three(エクスペリア ワン マークスリー) | Xperia(エクスペリア)公式サイト". xperia.sony.jp (in Japanese). Retrieved 2021-07-28 .
- ^ "How does the 4K display work in Xperia i or Xperia i II ?". sony.com . Retrieved 2021-07-28 .
- ^ "Leading Television Manufacture Players Line Up To Support '4K Ultra HD'" (Printing release). Consumer Electronics Association. 11 Nov 2014. Archived from the original on 23 September 2015. Retrieved 18 December 2014.
- ^ Lowensohn, Josh (9 July 2010). "YouTube now supports 4k-resolution videos". Tech Civilization. CNET. Retrieved eighteen December 2014.
- ^ Brown, Heather (16 Oct 2014). "Good Question: When Volition We See Broadcasts In 4K?". Local. CBS Minnesota. Retrieved xviii Dec 2014.
- ^ "Canadian Serial Entrepreneur to Launch Beginning iv,000-pixel Tv set Signal, Bulb TV". 11 April 2013. Archived from the original on 2013-08-12. Retrieved 12 November 2013.
- ^ "Young media mogul granted TV licence". 12 Apr 2013. Archived from the original on 14 May 2013. Retrieved 12 Nov 2013.
- ^ "Canadian Cat B Channel Plans 4K Video Feed". xvi April 2013. Retrieved 12 November 2013.
- ^ "Bulb Television receiver to turn on 4k". 12 April 2013. Retrieved 12 November 2013.
- ^ "Broadcasting Decision CRTC 2012-268". iv May 2012.
- ^ Luckerson, Victor (12 November 2014). "Amazon Will Stream in Ultra-Loftier Def 4K by January". Tech Companies. Time. Retrieved xviii December 2014.
- ^ Anderson, Jim (17 December 2014). "4K Ultra HD, Loftier Quality: Ruddy". YouTube. Retrieved 18 December 2014.
- ^ Cox, Joe (27 June 2013). "Seiki launches 39in 4K Telly for $699". What Hi-Fi. Haymarket. Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- ^ Greenwald, Will (28 June 2013). "Seiki SE39UY04". PC Mag. Ziff Davis. Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- ^ "Viewsonic monitor". Newegg.com . Retrieved 21 November 2015.
- ^ "Call for Proposals for ATSC-3.0 Physical Layer" (PDF). Advanced Television Systems Committee. March 26, 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on May nine, 2013. Retrieved April 15, 2013.
- ^ "Advanced Television Systems Committee Invites Proposals for Next-Generation TV Dissemination Technologies". Advanced Boob tube Systems Committee. March 26, 2013. Archived from the original on April ane, 2013. Retrieved Apr 15, 2013.
- ^ "ATSC seeks proposals for ATSC 3.0 physical layer". Broadcast Engineering. March 27, 2013. Retrieved Apr 15, 2013.
- ^ Doug Lung (March 28, 2013). "ATSC Seeks Next-Gen TV Physical Layer Proposals". Idiot box Engineering. Archived from the original on 2013-05-20. Retrieved Apr 15, 2013.
- ^ "Applied science Group iii". Avant-garde Tv set Systems Commission. Retrieved October 11, 2016.
- ^ "GatesAir: Are y'all set for ATSC three.0?". GatesAir. Retrieved 8 November 2016.
- ^ "ATSC Standard: Video" (PDF). Advanced Tv set Systems Committee. Feb xiv, 2019. Retrieved February 28, 2019.
- ^ Rivington, James (July 7, 2014). "4K Tv set channels on the way as DVB-UHDTV standard is approved". TechRadar. Future Publishing Limited. Retrieved April 29, 2018.
- ^ a b c "Phasing in Ultra High Definition" (PDF). world wide web.dvb.org. DVB Project Role. February 2017. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 22, 2018. Retrieved Apr 29, 2018.
- ^ "DVB On Course for Future UHDTV System" (PDF). world wide web.dvb.org. Geneva: DVB Projection Office. November 18, 2015. Retrieved April 29, 2018.
- ^ Jukic, Stephanie. "4K & Ultra Hard disk Resolution". 4K.com. Archived from the original on xxx July 2019. Retrieved 26 November 2014.
YouTube has had a 4K channel running since as early on as 2010 and other developments are definitely on the horizon, especially in countries or regions with excellent internet connectivity that goes above the normal speeds available to most people.
- ^ Sarukkai, Ramesh (2010-07-09). "What's bigger than 1080p? 4K video comes to YouTube". Archived from the original on xvi July 2011. Retrieved 2011-08-20 .
- ^ "Advanced encoding settings". Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- ^ Ohannessian, Kevin. "Where Can You Get 4K Video?". Toms's Guide. Purch, Inc. Retrieved 26 November 2014.
YouTube and Vimeo already stream 4K content. Near of the videos are of the nature/documentary diverseness, with some tech media coverage thrown in the mix. Withal, Google recently announced plans to make a much larger option of 4K video available on YouTube, using its new compression technology, called VP9. If your computer has a powerful graphics menu that supports 4K and HDMI version 1.4 or higher, you lot can connect your estimator to a 4K telly via an HDMI cable. You will likely demand high bandwidth to stream the video without whatever issues, though neither YouTube nor Vimeo has specified the minimum information speed needed for 4K streaming. Asus, Dell, Sharp, and others make 4K figurer monitors.
- ^ Anderson, Jim. "4K Ultra Hd Test, Loftier Quality Bluish". YouTube. Retrieved i April 2015.
- ^ Lawler, Ryan (25 Jan 2013). "Next-Gen Video Format H.265 Is Canonical, Paving The Way For High-Quality Video On Depression-Bandwidth Networks". TechCrunch. AOL. Retrieved 30 May 2014.
- ^ "Naughty America: 4K porn is coming, trailer released", Pocket lint, 2014-01-13
- ^ "Payserve Launches 4k Ultra-Hd Site, Sindrive". Developed Video News . Retrieved 23 Jan 2016.
- ^ "4K Video Recording at 60fps on phones is here but information technology comes with a catch". two June 2018. Retrieved June 2, 2018.
- ^ a b GPU History: Hitachi ARTC HD63484. The 2d graphics processor. (IEEE Computer Society)
- ^ Frost, Jacqueline B (2009). Cinematography for Directors: A Guide for Creative Collaboration. Michael Wiese Productions. p. 199. ISBN978-one-61593019-7 . Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- ^ "Dalsa Origin was the very first commercially obtainable 4K Resolution". epfilms . Retrieved nineteen June 2016.
- ^ Ramsey, Doug (Aug 24, 2009). "Moving-picture show Premiere in Cyberspace Links Brazil, U.S. and Nihon". Retrieved May 24, 2018.
- ^ a b Teoh, Vincent (25 Dec 2013). "YouTube Adds "2160p 4K" Option To Video Quality Settings". HDTVTest . Retrieved 24 May 2014.
- ^ "Youtube puts in new 2160p 4K selection for video-settings". Neo win. Retrieved 24 July 2014.
- ^ Truong, Alice (August half dozen, 2013). "4K is already playing at a theater near yous, merely y'all probably didn't fifty-fifty notice". Digital Trends. Designtechnica. Retrieved 24 May 2014.
- ^ "Sony Unveils New "4k" Digital Cinema Projector" (press release). Projector Central. June 3, 2004. Retrieved 24 May 2014.
- ^ Quick, Darren (May 31, 2012). "Sony releases world's showtime 4K habitation theater projector". Gizmag . Retrieved 24 May 2014.
- ^ Schodt, C. (June xix, 2019). "Why your Avengers UHD Blu-rays aren't actually 4K". Engadget . Retrieved May 10, 2021.
- ^ Denison, Caleb (September iv, 2013). "Sony feeds starving 4K early adopters with over 70 titles of 4K movies and TV shows". Digital Trends . Retrieved 31 May 2014.
- ^ "Breaking Bad is at present streaming in 4K on Netflix", Gizmodo
- ^ Katzmaier, David (eight Apr 2014). "Netflix begins 4K streams". CNET . Retrieved xxx May 2014.
- ^ Kerr, Dara (17 Dec 2013). "Amazon Studios to brainstorm shooting original series in 4K". CNET . Retrieved 30 May 2014.
- ^ "List of 4k UHD Movies & Goggle box Shows on Amazon Video – Hard disk drive Written report". hd-written report.com . Retrieved 2017-11-25 .
- ^ "The beginning ever Ultra HD 4K Blu-ray player has gone on sale a little fleck early on". The Verge . Retrieved 2017-11-25 .
- ^ Machkovech, Sam (August two, 2016). "Microsoft hid performance boosts for sometime games in Xbox One S, told no one". Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Retrieved June 17, 2019.
- ^ Layden, Shawn (2016-xi-10). "PlayStation iv Pro Launches Today". blog.us.playstation.com . Retrieved November x, 2016.
- ^ "The PS4 Pro, every bit explained past the man who designed it". Engadget . Retrieved June 17, 2019.
- ^ "Xbox One X review". The Verge . Retrieved 2017-xi-25 .
- ^ "Xbox Ane X Enhanced Games List | HDR, Ultra HD, & 4K Gaming". Xbox.com . Retrieved June 17, 2019.
- ^ Katzmaier, David (March thirty, 2015). "Sony VPL-VW350ES review". CNET . Retrieved December seven, 2015.
- ^ Pendlebury, Ty (September 26, 2013). "JVC debuts cheaper pseudo-4K projectors". CNET . Retrieved December 7, 2015.
- ^ "DLA-X550R Overview". JVC. Retrieved December 7, 2015.
- ^ Silva, Robert (Oct xvi, 2015). "JVC Intros fourth Generation eastward-Shift 4K Projectors at CEDIA 2015". Well-nigh.com. Retrieved December seven, 2015.
- ^ Cohen, Steven (October 19, 2015). "JVC Readies New eShift 4K D-ILA Projectors with HDR". High-Def Digest. Retrieved December 7, 2015.
- ^ Turnbull, Grant (Nov 25, 2015). "I/ITSEC 2015: New grooming approaches for Boeing". Shephard Media. Retrieved December 7, 2015.
- ^ "4K Ultra Hard disk: Into the Vaults—Prepping Films for 4K Ultra Hd is a Journeying of Discovery – Media Play News". Retrieved 2020-10-28 .
- ^ "DirecTV launches 4K sectional to Samsung TVs". CNET . Retrieved 15 April 2016.
- ^ "BT Sport Ultra Hard disk drive Made Even My Mum Want to Scout 4K Football game". Gizmodo Uk . Retrieved 24 January 2016.
- ^ "Behind the scenes of BT Sport'southward 4K Ultra Hard disk revolution". Techradar. Archived from the original on 29 Jan 2016. Retrieved 23 January 2016.
- ^ a b "4K content becomes a reality in Canada". Toronto Star . Retrieved 21 January 2016.
- ^ "Why y'all should add a 4K television to your holiday shopping listing". The World and Postal service . Retrieved xvi January 2016.
- ^ a b "TSN delivers alive 4K broadcast of Raptors-Celtics". TSN.ca. xiii January 2016. Retrieved 15 January 2016.
- ^ "Rogers leveraging sports ownership to push 4K TV". The Earth and Mail . Retrieved 6 October 2015.
- ^ "Rogers announces Ignite Gigabit cyberspace, 4K sports broadcasts". CBC News . Retrieved 16 January 2016.
- ^ "4K Sports Descend on Canada: Starting time-Ever Alive 4K NBA Game From London Kicks Off Parade of 4K Content". Sports Video Group. 13 January 2016. Retrieved 16 January 2016.
- ^ "Sportsnet to produce first NHL game in 4K". Sportsnet.ca. Rogers Media. Retrieved 24 January 2016.
- ^ "Dome Productions Preps for Arrival of Alive 4K Sports in Canada". Sports Video Group. 15 January 2016. Retrieved 16 Jan 2016.
- ^ "Dome, Rogers Sportsnet Develop Unmarried Production Solution for UHD/HD". Sports Video Group. 12 April 2016. Retrieved 21 April 2016.
- ^ "Juno Awards 2016: The Weeknd, Bieber, Dean Brody among winners". CBC News . Retrieved 21 April 2016.
- ^ "SVG Exclusive: Univision to produce Copa América Centenario final in 4K". Sports Video Group Europe. Archived from the original on 12 March 2016. Retrieved 12 March 2016.
- ^ "How Univision is chirapsia the competition to 4K sports streaming". Engadget . Retrieved 12 March 2016.
- ^ "Mexico vs Senegal friendly is a test for 4K". TechRadar. Archived from the original on 12 March 2016. Retrieved 12 March 2016.
- ^ "DirecTV's first alive 4K evidence is the Masters golf tournament". Engadget . Retrieved 12 March 2016.
- ^ "The Masters in 4K: DirecTV, CBS Sports Tee Upwards First Live 4K UHD Broadcast in U.Due south." Sports Video Grouping. nine March 2016. Retrieved 12 March 2016.
- ^ "Telus clears up picture with new 4K offerings". Press Reader.
- ^ "FIFA Confederations Cup Testing 4K; Might Lead to World Loving cup 'Ultra Hard disk drive' Broadcast". The Hollywood Reporter . Retrieved 2018-11-24 .
- ^ "4K Idiot box misses its World Cup goal". The Verge . Retrieved 2018-eleven-24 .
- ^ "Fob, Telemundo Offering a Clearer View of FIFA World Loving cup Russia". Tv Engineering science . Retrieved 2018-xi-24 .
- ^ "Globe Cup 2018: BBC to show tournament in Ultra HD & virtual reality". BBC Sport. 2018-05-30. Retrieved 2018-xi-24 .
- ^ "FuboTV streaming Globe Cup in 4K resolution". SportsPro . Retrieved 2018-11-24 .
- ^ Cohen, David S. (1 August 2013). "Ultra-HD TV Faces Bandwidth Challenge to Get Into Homes". Variety . Retrieved 30 May 2014.
- ^ "Resolution Table". Pixar. Retrieved 21 Jan 2014.
- ^ "4K resolution Definition from PC Magazine Encyclopedia". PC Magazine. 1994-12-01. Archived from the original on 2010-03-26. Retrieved 2010-05-28 .
- ^ James, Jack (2006). Digital Intermediates for Motion-picture show and Video. Taylor & Francis. p. 125. ISBN0240807022 . Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- ^ "Canon DP-V3010 4K Reference Display" (PDF). Canon. Retrieved April 29, 2018.
- ^ Chester, Brandon (October 27, 2016). "LG Introduces New UltraFine 4K and 5K Monitors". Anandtech. Anandtech. Retrieved Apr 29, 2018.
- ^ Novakovic, Nebojsa (March 28, 2003). "IBM T221 - the earth'southward finest monitor?". The Inquirer. Incisive Business Media (IP) Limited. Archived from the original on September fourteen, 2009. Retrieved April 29, 2018.
{{cite spider web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Tanous, Jim (March 13, 2018). "3840x1600 Ultrawide Monitors: How 160 Lines Tin Make All the Departure". PC Perspective . Retrieved April 29, 2018.
- ^ "LG 38UC99-W Ultrawide Monitor". Retrieved April 29, 2018.
- ^ "Acer XR382CQK bmijqphuzx (UM.TX2AA.001)".
- ^ Singleton, Micah (June 14, 2017). "Dell'southward latest ultrawide monitor is a 38-inch curved beast". The Verge . Retrieved Apr 29, 2018.
- ^ Thacker, Jim (September 17, 2017). "HP announces new 37.v-inch curved Z38c brandish". CG Aqueduct. Archived from the original on January 12, 2018. Retrieved Apr 29, 2018.
- ^ Lilly, Paul (June 9, 2017). "Samsung launches insanely broad 32:9 aspect ratio monitor with HDR and FreeSync 2". PC Gamer . Retrieved April 29, 2018.
- ^ a b Wootton, Cliff (2005). A Applied Guide to Video and Audio Pinch: From Sprockets and Rasters to Macroblocks. Taylor & Francis. p. 47. ISBN0-24080630-1 . Retrieved 21 Jan 2014.
- ^ Braverman, Barry (2013). Video Shooter: Storytelling with Hard disk drive Cameras. CRC Printing. pp. 4–18. ISBN978-1-13605885-1 . Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- ^ Sawicki, Mark (2007). Filming the Fantastic: A Guide to Visual Effects Cinematography. CRC Press. p. 114. ISBN978-1-13606662-7 . Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- ^ Poynton, Charles. "YUV and luminance considered harmful: A plea for precise terminology in video" [1]
- ^ "Why 4K video looks better on a 1080p screen" . The Daily Note.
- ^ Babcock, Adam (2019-03-04). "Blush Subsampling: 4:4:4 vs 4:two:ii vs iv:ii:0". RTINGS.com . Retrieved two August 2020.
External links [edit]
Articles [edit]
- "3D Goggle box is Expressionless, Long Live 4K", Forbes, Jan 10, 2013
- Gurule, Donn, 4k and 8k Product Workflows Become More Mainstream, Light axle, archived from the original on 2013-02-16, retrieved 2013-01-29
- What is the meaning of UHDTV and its departure to HDTV?, UHDMI, archived from the original on 2013-02-05, retrieved 2014-09-ten
- "Ultra high resolution television (UHDV) prototype", CD Freaks, archived from the original on 2008-11-eighteen, retrieved 2013-01-29
- "Just Like High-Definition TV, but With College Definition", The New York Times, Jun 3, 2004
- "Nihon demonstrates next-gen TV Circulate", Electronic Engineering Times, archived from the original on 2013-05-01, retrieved 2013-01-29 .
- "Researchers arts and crafts HDTV'due south successor", PC World, archived from the original on 2008-06-04, retrieved 2013-01-29
- Sugawara, Masayuki (2008), Super Hello-Vision—research on a future ultra-HDTV system (PDF) (technical review), CH: EBU, archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-03-26, retrieved 2013-01-29
- Brawl, Christopher Lee (Oct 2008), "Farewell to the Kingdom of Shadows: A filmmaker'southward first impression of Super Hello-Vision television set", Musings, archived from the original on 2013-03-23, retrieved 2013-01-29
- "Visual comparing of the unlike 4K resolutions", 4k Tv, archived from the original on 2014-08-10, retrieved 2014-08-08
- "Why Ultra HD 4K TVs are nonetheless stupid", CNet , 2015 follow-up commodity: "Why 4K TVs aren't stupid (anymore)", CNet
Official sites of NHK [edit]
- Super Hi-Vision, JP: NHK, archived from the original on 2010-x-06, retrieved 2013-01-29 .
- Science & Technical Enquiry Laboratories, JP: NHK .
- Super Hi-Vision research (annual report), JP: NHK STRL, 2009, archived from the original on 2012-10-18, retrieved 2013-01-29 .
Video [edit]
- "4K resolution video exam sequences for Inquiry", Ultra video, FI: TUT .
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/4K_resolution
Posted by: powelltheretion.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Does The Camera In My Samsung J3 Have Image Stabilization"
Post a Comment